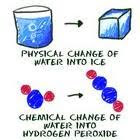
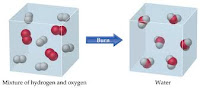
Preassure: the force on each unit of area of a surface.

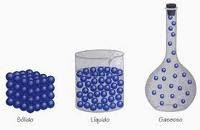
Melting: the change of solid into a liquid.

Vaporization: the change of a liquid to a gas as molecules break free from each other.

Condensation: the change of a gas into a liquid as molecules attrack each other.
Freezing: the change of a solid into a liquid.

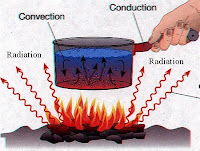
Boiling: the formation of bubbles of vapor the escape from a liquid that is being heated.
Evaporation: the vaporization of molecules from the surface of a liquid.